Cloud Services




Cloud Services
Cloud services refer to the delivery of computing resources (such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, etc.) over the internet, commonly referred to as "the cloud." Rather than owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure, businesses and individuals can access these services from cloud providers on a pay-as-you-go basis. This offers significant cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and ease of access, making cloud services a cornerstone of modern IT strategy.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services can be broadly categorized into three main types, based on the level of control and management required:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It allows businesses to rent IT infrastructure such as servers, storage, networking, and other computing resources on-demand.
Use Cases: Hosting websites, running virtual machines, developing and testing applications, backup, and disaster recovery.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective as businesses only pay for the resources they use.
- Flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- No need for physical hardware management.
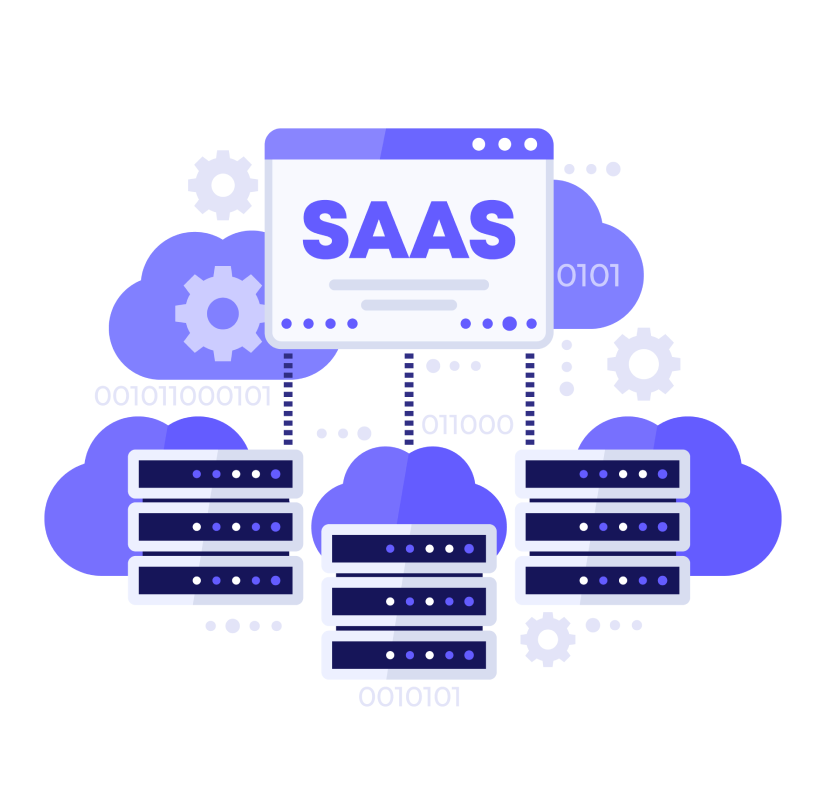
2. Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. These applications are fully managed and hosted by the cloud provider, with users accessing them via a web browser or app.
Use Cases: Email, collaboration tools, customer relationship management (CRM), and enterprise resource planning (ERP).
Benefits:
- No installation or maintenance required for end-users.
- Accessible from any device with an internet connection.
- Regular updates and improvements handled by the provider.

Deployment Models of Cloud Services
Cloud services are also classified based on their deployment model, which dictates who manages the infrastructure and how it's accessed:
Public Cloud
Public cloud services are owned and operated by third-party providers and are available to the general public. Resources such as storage, servers, and applications are shared among multiple customers, often referred to as multi-tenancy.
Use Cases:Small businesses, startups, organizations with fluctuating demand, or those seeking low-cost options.
Benefits:
- Cost-effective with no maintenance or infrastructure management.
- Scalable and flexible for various needs.
- Wide range of services and tools available.

Private Cloud
A private cloud is a cloud infrastructure used exclusively by one organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider but offers more control over security and customization compared to public cloud services.
Use Cases:Enterprises with strict regulatory or compliance requirements, or those needing complete control over their infrastructure.
Benefits:
- Greater control over security and data privacy.
- Customizable for specific business needs.
- Suitable for highly regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare).

Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines both public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model gives businesses more flexibility to scale their workloads while maintaining control over sensitive data.
Use Cases:Businesses that need to keep critical workloads on private infrastructure while leveraging public cloud services for less-sensitive operations.
Benefits:
- Flexibility to move workloads between public and private clouds.
- Optimizes cost and performance.
- Ensures compliance by maintaining sensitive data on private infrastructure while benefiting from the scalability of public clouds.

Benefits of Cloud Services:
1. Cost Efficiency:
Traditional IT infrastructure requires heavy upfront capital investment in hardware, software, and facilities. Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go or subscription model, allowing businesses to only pay for what they use and avoid hefty upfront costs.
No need for maintenance or upgrades, as the cloud provider manages everything.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
Cloud resources can be scaled up or down based on demand. This makes it ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads or those experiencing growth.
Cloud services support rapid deployment of new services, features, or systems.
3. Accessibility:
Cloud services can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. This supports remote work, global operations, and collaboration.
Cloud platforms typically offer 24/7 access to data and applications from anywhere in the world.
4. Security and Compliance:
Cloud providers often have advanced security measures in place, such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular security audits. They also offer compliance with various regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
Data backup and disaster recovery capabilities are also integrated into cloud services, ensuring minimal downtime.
5. Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
Cloud providers handle software updates, patches, and hardware maintenance, reducing the burden on internal IT teams and ensuring systems are always up-to-date and secure.
This allows businesses to focus on their core activities rather than managing infrastructure.
6. Collaboration and Innovation:
Cloud services enable easy collaboration by providing centralized access to data, tools, and applications. Teams can work together in real-time, share files, and collaborate across geographies without the need for complex setup.
Cloud computing fosters innovation by allowing businesses to experiment and deploy new ideas quickly.
