There are two types of hardware devices which are commonly used for data backups :
NAS
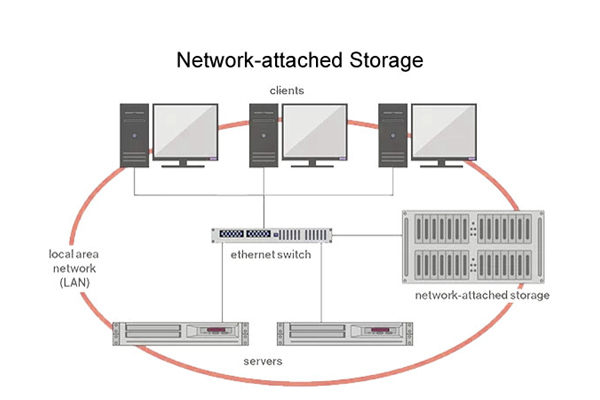
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS is specialized for serving files either by its hardware, software, or configuration.
SAN
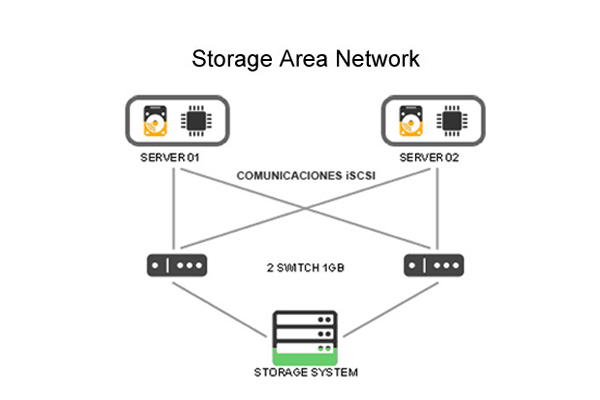
A storage area network (SAN) is a network which provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to enhance storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as locally attached devices.
SANs typically utilizes Fiber Channel connectivity, while NAS solutions typically use TCP/IP networks, such as Ethernet. But the real difference is in how the data is accessed. A SAN accesses data as blocks, while a NAS accesses data as files. Storage architects will choose one over the other based on the type of data being stored and which architecture will provide the highest level of performance.
In enterprises, where it is necessary to support numerous high-speed file transfers involving terabytes of files, SAN is generally the best option. A single SAN with a high-performance disk array can offer the scalability and performance necessary to handle those kinds of workloads.